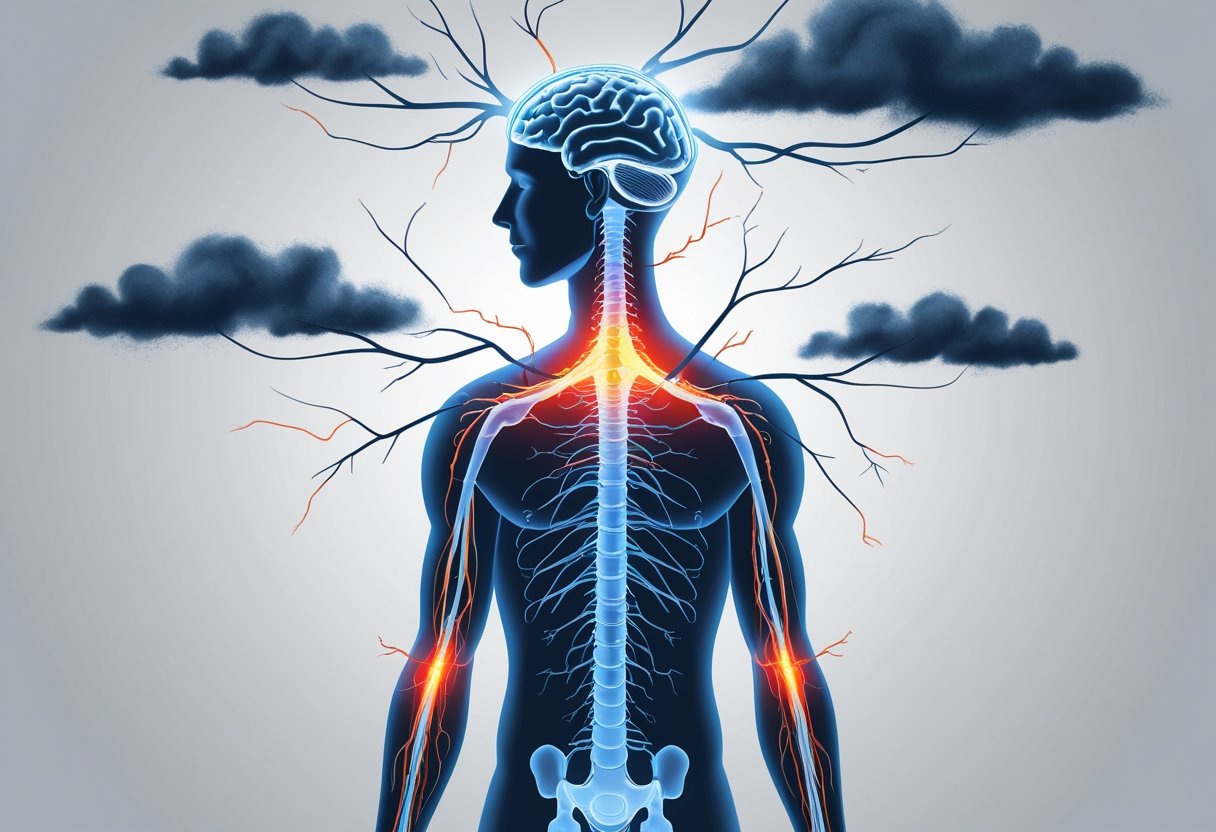
Stress is more than just a mental burden; it can profoundly affect your physical health, particularly your nervous system. Chronic stress can exacerbate nerve pain and contribute to conditions such as neuropathy, leading to symptoms like tingling, burning, and discomfort. Understanding this connection is vital for anyone dealing with unexplained nerve pain or seeking effective management strategies.
As you navigate daily challenges, it’s crucial to recognize the ways stress manifests physically. The physiological changes your body undergoes in response to stress can intensify existing nerve issues and hinder healing. By addressing both the mental and physical aspects of stress, you can work toward alleviating those nerve-related symptoms and improving your overall well-being.
If you find that anxiety and stress are impacting your life, seeking support can make a significant difference. Tides Mental Health offers therapy that focuses on managing stress and its effects, helping you reclaim your peace of mind and reduce nerve pain. With options available for both in-person and virtual sessions in the Chicago area, you’re not alone in facing these challenges.
How Stress Triggers and Worsens Nerve-Related Pain
Stress plays a significant role in nerve-related pain by influencing the nervous system and the body’s stress response. Understanding how stress hormones affect nerve health is crucial for comprehending the connection between emotional well-being and physical discomfort.
The Stress Response and the Nervous System
When you encounter stress, your body activates the stress response system. This involves the adrenal glands releasing hormones, primarily adrenaline and cortisol.
- Adrenaline prepares your body for a fight-or-flight reaction, increasing heart rate and blood flow.
- Cortisol, often called the stress hormone, helps regulate metabolism and immune responses.
However, prolonged exposure to these hormones can lead to neuroinflammation, which directly affects nerve sensitivity. This heightened state of alertness can make your nerves more reactive, amplifying sensations of pain, particularly if you already suffer from conditions like neuropathy.
Physiological Changes That Affect Nerves
Stress induces several physiological changes that impact your nerve health. High cortisol levels can cause inflammation and reduced blood flow to the nerves, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Increased inflammation: This can lead to nerve damage over time.
- Altered pain perception: Chronic stress can change how your brain interprets pain signals, making you more sensitive.
Additionally, the prolonged release of stress hormones can disrupt neurotransmitter balance, leading to feelings of anxiety or depression, which further exacerbate physical symptoms.
Acute vs. Chronic Stress Effects on Nerve Health
The effects of stress on your nerves can vary significantly based on whether the stress is acute or chronic.
Acute stress can trigger temporary nerve pain but often resolves once the stressor is removed. Short bursts of stress can enhance focus and performance, but they may also lead to momentary discomfort due to increased adrenaline.
Chronic stress, on the other hand, poses a more significant risk. Sustained exposure to high levels of cortisol and neuroinflammation can lead to lasting nerve damage. It increases the risk of developing chronic conditions and can make existing pain more intense.
Recognizing these patterns can help you manage stress better and potentially reduce nerve-related pain, helping you reclaim your comfort and well-being. If you find yourself struggling with stress and its effects, consider seeking support. Tides Mental Health offers tailored therapy solutions suitable for various needs.
Stress-Induced Symptoms: Neuropathy and Beyond
Stress can manifest in various physical symptoms, significantly affecting your nervous system. Understanding how anxiety and tension contribute to sensations like tingling, pain sensitivity, and fatigue can help you manage these distressing experiences effectively.
Tingling, Numbness, and Burning Sensations
When stress levels rise, your body reacts in ways that may cause sensations such as tingling, numbness, and burning. These symptoms often arise from heightened anxiety, leading to increased muscle tension and blood flow changes. Issues like hyperventilation can exacerbate these feelings, creating a cycle of discomfort.
For many, these sensations may occur in the extremities, such as your hands and feet. Chronic stress can also trigger neuropathy symptoms, leaving you more sensitive to touch. Recognizing these stress-induced symptoms allows for better coping strategies and treatment options.
Neuropathy Symptoms Versus Actual Nerve Damage
Understanding the distinction between stress-induced symptoms and actual nerve damage is crucial. Neuropathy usually results from conditions such as diabetes or physical injuries. In contrast, stress exacerbates existing symptoms rather than causing new nerve damage directly.
Chronic stress can lead to heightened perception of pain, or neuropathic pain, even without underlying physical issues. This pain affects your quality of life and may develop alongside traditional nerve damage issues. Keeping this distinction in mind can guide you in seeking appropriate help for both anxiety and nerve-related concerns.
Pain Sensitivity and Fatigue
Stress significantly influences your sensitivity to pain, often leaving you feeling drained and fatigued. Chronic tension can lead to increased levels of cortisol, which amplifies your pain response. This heightened sensitivity can make ordinary sensations feel more intense and uncomfortable.
Moreover, stress can sap your energy, making fatigue a common companion. You might find it hard to engage in daily activities or experience cognitive fog. Addressing these symptoms through relaxation techniques, therapy, and support, such as those offered by Tides Mental Health, can help reduce their impact on your life.
Mechanisms Linking Stress and Nerve Dysfunction
Stress impacts the nervous system through various pathways, leading to nerve dysfunction. Understanding these mechanisms is vital to managing stress-related nerve pain effectively. The following sections explore how inflammation, muscle tension, and reduced blood flow contribute to nerve issues.
Inflammation and Neuroinflammation
Chronic stress triggers inflammation, affecting both the immune and nervous systems. This inflammation can lead to neuroinflammation, which specifically targets the brain and spinal cord. You may experience increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to damaged nerve cells.
This process plays a crucial role in conditions such as peripheral neuropathy, where nerve damage results from persistent inflammation. Inflammation alters pain signaling, making you more sensitive to pain and leading to persistent discomfort. Managing stress is essential to reduce these inflammatory markers and promote nerve health.
Muscle Tension and Nerve Compression
When you experience stress, your muscles often tighten, leading to increased muscle tension. This tension can compress nearby nerves, resulting in pain or discomfort. Common areas affected include the neck, shoulders, and back where muscle strain can irritate peripheral nerves.
As stress continues, the cycle of muscle tension and nerve compression can lead to chronic pain syndromes. For example, conditions like sciatica may arise when muscles in the lower back compress the sciatic nerve. Addressing stress through techniques such as relaxation exercises can alleviate muscle tension and reduce nerve-related pain.
Reduced Blood Flow to Peripheral Nerves
Stress can lead to reduced blood flow to peripheral nerves, impairing their function. When blood flow decreases, nerves receive less oxygen and nutrients, which are essential for proper nerve function. This situation can contribute to feelings of numbness or tingling in your extremities.
Over time, this diminished blood supply may result in further nerve damage. Improved circulation is vital for recovery, and stress management techniques can help restore normal blood flow. Regular exercise, even simple activities, promotes blood circulation and supports nerve health in response to stress.
The Role of Anxiety, Sleep, and Lifestyle Factors
Anxiety, sleep disturbances, and lifestyle choices play significant roles in nerve-related pain. Understanding how these elements interact can help you manage symptoms effectively and improve your overall well-being.
Anxiety and Overactive Nerve Firing
Anxiety often leads to heightened nerve sensitivity. When you are anxious, your body may enter a state of hyperarousal, causing your nerves to fire more readily. This increased nerve firing can lead to sensations like tingling or burning, similar to neuropathic pain.
The stress response triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which can exacerbate muscle tension. As your muscles tighten, they may compress nerves, contributing to pain and discomfort. Managing anxiety through techniques such as mindfulness, therapy, or breathing exercises can help reduce this overactivity. Tides Mental Health offers a variety of options for those seeking support with anxiety.
Sleep Disturbances and Nerve Pain
Sleep disturbances are common among those experiencing anxiety. Poor quality sleep can amplify feelings of pain and contribute to muscle weakness. When you sleep, your body repairs itself, including nerve health. Disrupted sleep prevents optimal recovery.
Lack of restorative sleep heightens sensitivity to pain and can create a vicious cycle where anxiety about pain leads to further sleep issues. Creating a sleep-friendly environment, maintaining a consistent bedtime, and considering relaxation techniques can help improve sleep quality. This is essential for minimizing pain levels and promoting nerve health.
Physical Activity and Posture
Physical activity is crucial to maintaining nerve health and managing pain. Regular exercise boosts circulation and promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural pain relievers. Additionally, engaging in physical activity helps combat muscle weakness and improves overall strength.
Posture also plays a vital role in nerve function. Bad posture can place excess strain on muscles and nerves, heightening pain. Being aware of your posture, especially while sitting for long periods, can help alleviate tension. Incorporating stretches and strengthening exercises can further support your nerve health. Tides Mental Health can assist you in finding suitable lifestyle approaches to tackle these issues effectively.
Stress Management and Nerve Pain Relief Strategies
Managing stress is crucial for alleviating nerve-related pain. Implementing effective strategies can help you regain control over your well-being. Here are several focused techniques to consider.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation are proven techniques that foster relaxation and enhance mental clarity. By dedicating even a few minutes daily to these practices, you can cultivate a sense of calm.
- Mindfulness encourages paying attention to the present moment, which can de-escalate stress responses.
- Meditation can be as simple as focusing on your breath, allowing your mind to clear. Research indicates this can lower cortisol levels, thereby reducing anxiety and associated nerve pain.
Try incorporating guided meditations or mindfulness apps to help you establish a routine. This consistency can lead to long-term improvements in both stress and nerve health.
Breathing Exercises for Stress Reduction
Breathing exercises are a straightforward way to counter stress. Engaging in deep, controlled breathing can activate your body’s relaxation response.
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Place one hand on your chest and another on your abdomen. Inhale deeply through your nose, focusing on expanding your abdomen rather than your chest.
- 4-7-8 Technique: Inhale for 4 seconds, hold for 7, and exhale slowly for 8. This practice can help reduce tension throughout your body.
Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can enhance your mood and minimize nerve pain caused by stress.
Balanced Diet for Nerve Health
A well-rounded diet plays an integral role in managing stress and promoting nerve health. Nutritional choices can directly affect how your body handles stress.
- B Vitamins: Essential for nerve function, find these in whole grains, eggs, and leafy greens.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These can be found in fish and flaxseeds and may help combat inflammation and anxiety.
- Antioxidants: Consuming berries, nuts, and vegetables can protect your nervous system from oxidative stress.
Prioritizing balanced meals can stabilize your mood and improve your body’s resilience to stress, thereby reducing nerve pain.
Effective Stress Reduction Techniques
A variety of effective stress reduction techniques can empower you to handle daily pressures. Experimenting with these methods can uncover what works best for you.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activities like walking, yoga, or strength training. Exercise not only boosts mood but also helps reduce physical tension associated with stress.
- Social Connections: Building strong relationships with friends and family provides emotional support, essential for managing anxiety.
- Time Management: Organizing your tasks and setting clear priorities can alleviate feelings of overwhelm.
These techniques can become essential tools in your stress management arsenal, leading to reduced nerve pain and enhanced emotional well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding how stress connects to nerve-related pain is essential. Many people experience anxiety-related neuropathy, which can manifest in various symptoms and impact daily life. Addressing this issue involves effective management strategies and a better grasp of the condition.
What methods can alleviate nerve pain resulting from anxiety?
Several methods can help reduce nerve pain related to anxiety. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and relaxation exercises are beneficial. You may also consider therapies that focus on regulating nerve activity, like non-invasive treatments designed to ease stress-induced tension.
What are the common symptoms of anxiety-related neuropathy?
Symptoms of anxiety-related neuropathy often include tingling, burning sensations, or numbness in various parts of the body. Many individuals report these sensations especially in the hands and feet. Stress responses can exacerbate these symptoms, making management crucial for relief.
Is it possible for stress to contribute to nerve pain in specific areas such as the legs?
Yes, stress can contribute to nerve pain in specific areas, including the legs. Increased muscle tension from stress may lead to disrupted nerve function, causing discomfort. Chronic stress can also exacerbate underlying conditions that affect nerve health.
Which medications are most effective for treating nerve pain?
Common medications for treating nerve pain include neuropathic pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Options may include gabapentin or pregabalin, which target nerve pain specifically. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best medication for your situation.
How does chronic stress impact the occurrence of nerve pain throughout the body?
Chronic stress can heighten the occurrence of nerve pain by causing continuous muscle tension and altering nerve pathways. This ongoing stress response can lead to inflammation and sensitive nerve endings, resulting in persistent discomfort across different body areas.
What are the indications of nerve inflammation related to stress?
Indications of nerve inflammation related to stress may include increased pain, sensitivity, or changes in sensation. You might also experience more pronounced symptoms during stressful situations. Recognizing these signs can help you seek appropriate support and management techniques.